Google Tag Manager (GTM) enables you to track different events by defining variables, triggers, and tags. In this post, I explain how to track 404 errors using the DataLayer.
I assume you already have GTM installed and verified that it is working. If you haven’t done this, follow the setup instructions first.
Setting up your application
Setting up GTM in Laravel is possibly even easier than the manual installation. The people of Spatie have released a package to install GTM on your website and added a great way to configure the DataLayer variable.
Install spatie/googletagmanager using the documentation on the GitHub repository. Make sure to configure the GTM id from your environment configuration file, do not hard code it into config/googletagmanager.php. Read more on the proper use of configuration files in Laravel if you are not sure how to do this.
When you installed everything, you are able to set a variable in the DataLayer with GoogleTagManager::set('foo', 'bar'). In my ExceptionHandler I assign a errorcode variable containing the HTTP error code that was triggered, eg. GoogleTagManager::set('errorcode', '404');. Take a look a the full ExceptionHandler for more details.
Configure GTM
Now it’s time to login into Google Tag Manager and configure our variables, triggers and tags:
- Make a new user-defined variable called “errorcode”.
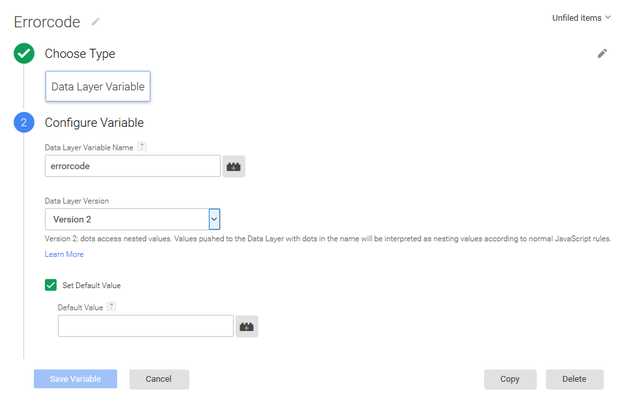
Set an empty default value (ie. “”) so that you can be sure the variable exists on every page.
- Create a new trigger called “Error code on page”.
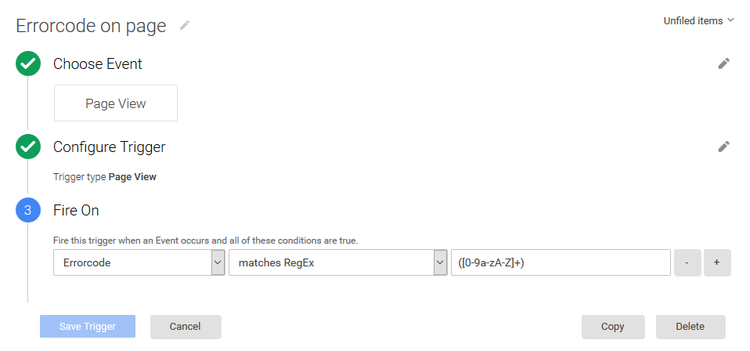
This trigger will, ehm, trigger when the errorcode variable is non-zero.
- Add a new tag called for tracking events when there is an errorcode on a page.
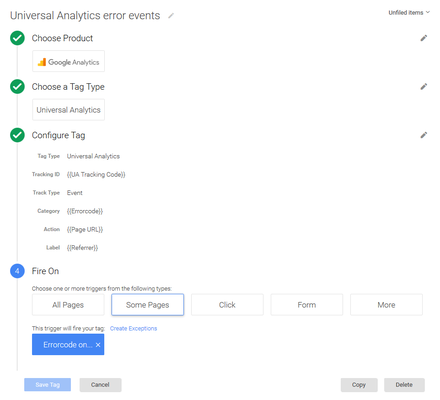
This tag uses our new variable as the name of our event. It is only called when our newly defined trigger matches.
The result
The result is that Google Analytics events are fired when an errorcode is found on the page. The category of the event will be the errorcode itself (eg. 404), the action of the event is equal to the URL that triggered the error and the label is equal to the referer URL.